Tiempo Climate Cyberlibrary
Global Energy Review 2003
- Tiempo archive
- Complete issues
- Selected articles
- Cartoons
- Climate treaty
- Latest news
- Secretariat
- National reports
- IPCC
About the Cyberlibrary
The Tiempo Climate Cyberlibrary was developed by Mick Kelly and Sarah Granich on behalf of the Stockholm Environment Institute and the International Institute for Environment and Development, with sponsorship from the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency.
While every effort is made to ensure that information on this site, and on other sites that are referenced here, is accurate, no liability for loss or damage resulting from use of this information can be accepted.
|
World carbon emissions from hydrocarbon use rose by 3.8 per cent in 2003, with about half the increase accounted for by China, according BP Chief Economist Peter Davies, reported in the July 2004 issue of Ecoal. Newswatch editor Mick Kelly reports. |
|
|
© BP |
|
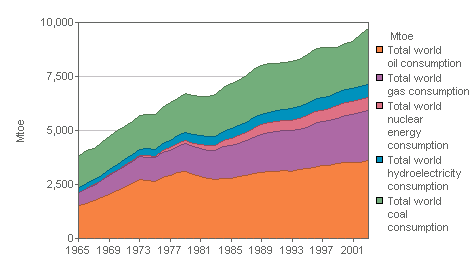
Global energy consumption, 1965-2003 |
|
Peter Davies was launching the latest BP Statistical Review of World Energy in the UK. The data show that global carbon emissions in 2003 stood 18 per cent above 1990 levels.
According to the Review, world primary energy consumption grew by 2.9 per cent in 2003 as a result of economic recovery. In China, energy consumption rose by 13.8 per cent, with coal consumption increasing by 15.2 per cent, as a result of strong economic growth. China is now the world’s second largest consumer of oil behind the United States.
"The challenge for China is to access global energy supplies at competitive prices and to create and apply appropriate technologies for transforming energy consumption, on which China's long term economic prosperity depends," said Byron Grote, managing director and chief financial officer of the BP Group at the launch of the report in China.
Worldwide, growth in coal consumption during 2003, at 6.9 per cent, was the second highest annual rise in this sector since 1984 and the highest during 2003 of any energy source.
Nuclear consumption fell by 2 per cent, largely as a result of a reduction in Japanese output as reactors were closed for safety checks. Renewable energy production continued to increase, with the fastest growth in the windpower and photovoltaic sectors. Biomass is the largest commercial source of renewable energy.
Further information
The full text of the
BP Statistical Review of World Energy 2004 is available
on-line, along with data files and analysis tools.
Bright Ideas

General Electric plans to cut solar installation costs by half

Project 90 by 2030 supports South African school children and managers reduce their carbon footprint through its Club programme

Bath & North East Somerset Council in the United Kingdom has installed smart LED carriageway lighting that automatically adjusts to light and traffic levels
The United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and the American Public Gardens Association are mounting an educational exhibit at Longwood Gardens showing the link between temperature and planting zones

The energy-efficient Crowne Plaza Copenhagen Towers hotel is powered by renewable and sustainable sources, including integrated solar photovoltaics and guest-powered bicycles
El Hierro, one of the Canary Islands, plans to generate 80 per cent of its energy from renewable sources

The green roof on the Remarkables Primary School in New Zealand reduces stormwater runoff, provides insulation and doubles as an outdoor classroom

The Weather Info for All project aims to roll out up to five thousand automatic weather observation stations throughout Africa

SolSource turns its own waste heat into electricity or stores it in thermal fabrics, harnessing the sun's energy for cooking and electricity for low-income families

The Wave House uses vegetation for its architectural and environmental qualities, and especially in terms of thermal insulation

The Mbale compost-processing plant in Uganda produces cheaper fertilizer and reduces greenhouse gas emissions

At Casa Grande, Frito-Lay has reduced energy consumption by nearly a fifth since 2006 by, amongst other things, installing a heat recovery system to preheat cooking oil
Updated: May 15th 2015